| Key Summary |
|
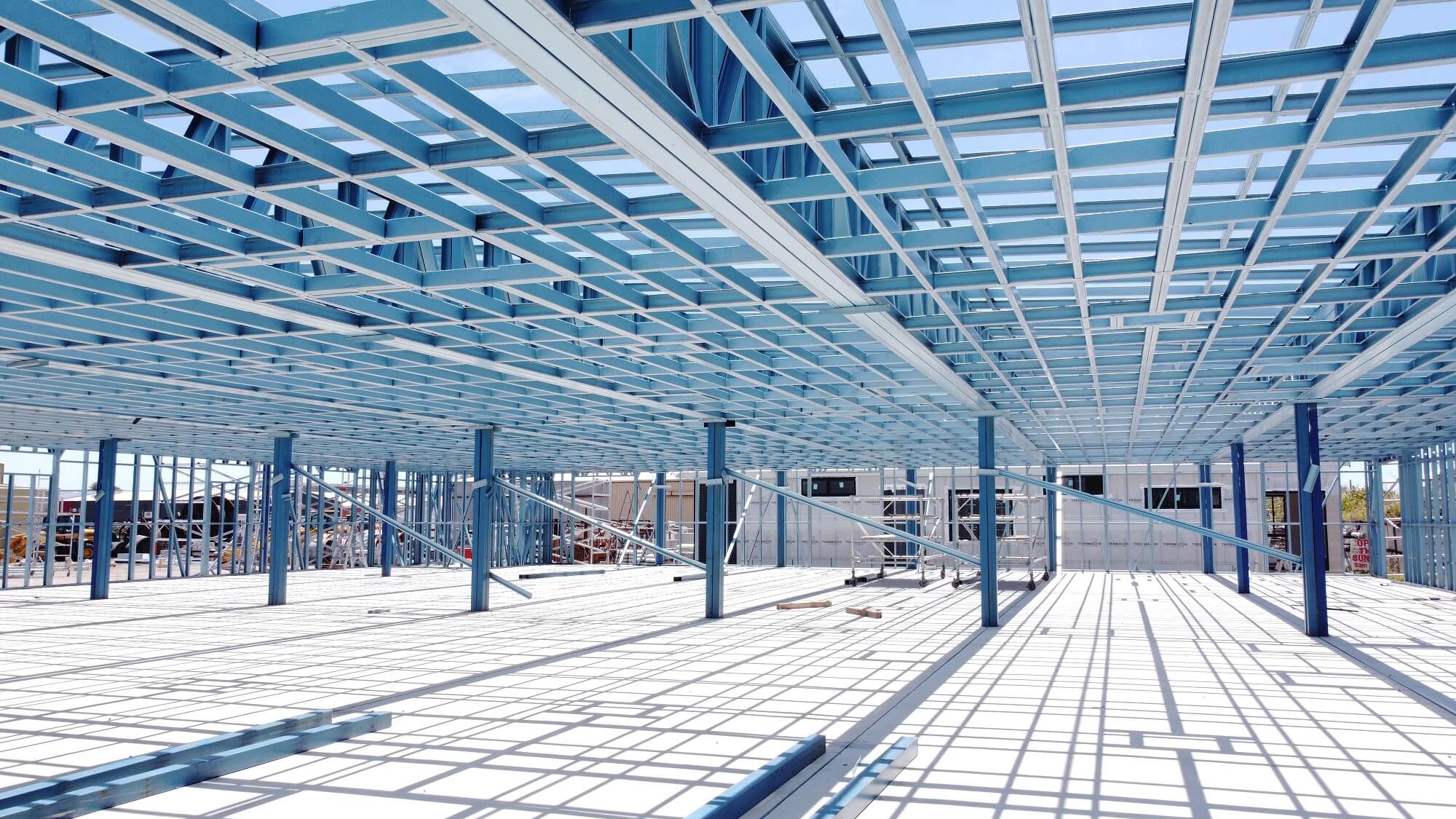
Light gauge steel framing (LGSF) is a type of construction technology that uses thin sheets of cold-formed steel as its construction material. Light steel framing can serve as a primary (such as webbed steel trusses) or secondary (such as steel studs) structures.
|
Builders today are building for the future. We’re in an era where innovation and sustainability must meet face-to-face. That’s why choosing the best materials and using innovative construction techniques have become more important than ever. Light gauge steel frames, for many builders, are a game-changer. The design is sleek and precise whilst staying environmentally friendly.
But the question remains: Is this modern marvel suitable for your next project? This blog will help you find out.
What is a Light Gauge Steel Frame?
If you’re a builder, you’ve likely heard of or used light gauge steel frames due to the boom in their popularity in residential and commercial construction over recent years. Light gauge steel framing (LGSF) is a type of construction technology that uses thin sheets of cold-formed steel as its construction material. Typically, these sheets are galvanised to resist corrosion. They remain lightweight, especially compared to wood, making transporting them to your construction site easy.
LGSFs are used for a variety of structures, such as:
- Roof systems
- Roof panels
- Wall systems
- Floor systems
- Decks
- Studs
- Headers
- Truss members
- Joists
Light steel framing can serve as a primary (such as webbed steel trusses) or secondary (such as steel studs) structure. This framing system is frequently used as a substitute for RCC or traditional buildings, as well.
How is a Light Gauge Steel Frame Built?
The construction process of light gauge steel frames requires precision and a keen eye for detail. It begins with a detailed architectural plan, which specifies the necessary aspects of the build, including the dimensions and layout. A structural engineer typically determines the steel frame specifications and other requirements.
LGSFs are created through cold forming, a process involving passing thin steel sheets through rollers and presses. Unlike hot-rolled steel, light gauge steel frames are shaped at room temperature. The result is a consistently shaped and designed steel frame.
For fire-damage prevention, steel is coated with zinc or sometimes combined with aluminium, known as “galvanised” steel. As mentioned, this coating also protects the material from corrosion and lasts 50 years. The coating can be thick or thin, depending on the intended purpose. For example, a thick layer is useful in humid locations, whilst a thin coat is more suitable for dry regions.
Key Characteristics and Components of Light Gauge Steel
Light gauge steel frames are made up of thin steel sheets, ranging from 1mm to 3mm for structural sections and 1mm to 2mm for non-structural units. Despite their thinness, they have an incredible strength-to-weight ratio, allowing them to bear heavy loads without looking bulky. Components of LGSF include:
- Load-bearing walls carry and transfer the weight of the building down to the foundation and the ground. They require strength and stability, essential to the structure’s integrity.
- Non-load-bearing walls are the internal walls that do not support the roof, floors, or any part of the structure and their loads. They’re typically used for dividing interior spaces and creating rooms.
- Wall cladding and partitions resist wind load with the help of polystyrene, gypsum board, and other similar materials, connecting them to the peripheral flange using a self-drilling screw.
- Wall openings comprise internal and external doors, as well as window frames.
- Wall connectors like nuts, washers, and bolts hold the structure together.
- Roof systems use structural steel, typically C75 and C100 grades. Builders can fasten LGSF directly into the wall frame for various roof designs, including gable, hip, and Dutch gable.
- Floor systems are generally made up of C-section joists connected to C-section bearers. LGSF provides better support for the floorboard, making it stiffer and more durable.
Studs, tracks, and joists are steel framing components, as well as connectors like clips and brackets. Insulation may be inserted between the framing members for thermal and acoustic insulation.
Light Gauge Steel Advantages vs. Other Framing Systems
Light gauge steel is just one of the several framing options in construction. Each has its advantages and disadvantages, so let us explore and compare them with other commonly used framing systems. LGSF offers the following:
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Strong and lightweight, steel framing is easy to transport and install whilst efficiently supporting loads and withstanding heavy weights.
- Precision-Engineered: Steel components have little to no onsite errors since they are built with a high degree of accuracy and control to meet specific standards and performance criteria.
- Flexibility: LGSF can be used in a variety of builds, including residential, commercial, industrial, and specialised construction like bridges and airports.
- Resilience: Incredible resistance to pests, rot, fire, and other damages makes steel a good choice for builders with longevity in mind.
- Sustainability: The material can be recycled endlessly without losing its original quality and strength.
Compared to wood and timber framing, light gauge steel is also more economical.
Wood is easy to find, as it is readily available and even offers natural insulation properties, unlike steel, which conducts heat. However, wood is extremely susceptible to pests and fire, particularly without special treatments. It does not last as long as steel. Often, there are concerns regarding sustainability and deforestation. The same applies to timber framing.
As for concrete or masonry framing, this framing system offers excellent fire resistance and high load-bearing capacities. However, unlike steel, it is often labour-intensive. You need to use heavy equipment and specialised machines to work with concrete blocks and masonry.
Common Applications of Light Gauge Steel
Light gauge steel framing can be used in a wide range of designs and layouts, as the frames can be customised to fit different building configurations. Steel is naturally sturdy, allowing architects and engineers to use it for complex structures like curved walls and volumetric modular pods. The frames are also excellent for:
- External cladding
- Interior office partitions
- Office buildings
- Residential houses and apartments
- Retail stores
- Warehouses and manufacturing facilities
- Educational facilities
- Healthcare facilities
- Sports arenas and stadiums
- Fitness centres
- Prefab and modular construction
Light gauge steel framing can reduce onsite waste and labour. Plus, steel is a durable material that requires little maintenance, which lowers costs even further. It is also resistant to rot, moisture, pest damage, and fire, making it a cost-effective choice for any build.
FAQs
- What is Light Gauge Steel Framing?
It’s a construction method using thin steel studs or sections for a durable building and structural framework while remaining lightweight.
- How Strong is Light Gauge Steel Framing?
It’s exceptionally strong with a high strength-to-weight ratio, allowing it to withstand heavy loads and provide structural integrity.
- How Long Does Light Gauge Steel Last?
Light gauge steel frames can last for several decades, especially with proper maintenance, extending their longevity for at least 50 years.